上回我們將使用者輸入的部分以及初始化的部分給完成了,這次接續將剩餘部分做完。將初始結點新增進open list之中,並確認初始結點是否為一個合法結點。若並非合法結點則直接輸入,讓使用者知道這種傳教士人數以及食人族人數的組合是沒有結果的。
open_list.append(init)
# check whether the initial state is legal
if (not (state.isLegal((init), state.BoatState(1, 1, 0, 0)))):
print("The condition doesn't have a solution.")
sys.exit()
若通過上述的檢驗後,我們接續就要開始真正的結點展開了。我們只要當open list中還有結點並未展開或是我們展開的結點中遇到了終點的話,我們才會終止迴圈。每次的迴圈執行都是從open list中取出一個結點進行展開,展開後將此結點放進closed list之中,並將他所展開的所有結點放入open list之中。由於我們展開結點以及結點的合法性是分開處理的,因此我們先利用addChild函式獲得展開結點並暫存於一個list之中,接著遍歷list去確認結點是否合法,若合法才放進closed list之中。最後我們的open list還要根據f值以及h值的大小進行排序,如此才能保證取到終點時獲得的是最短路徑。
另外我們為了讓結果能夠呈現結點展開的用時為多久,我們在迴圈開頭以及結尾利用變數儲存了時間紀錄,以利到最後結果呈現的部分可以計算出耗時。(讀者可以自由選擇是否要加入)
設計如下:
timeStart = time.time()
while(len(open_list) != 0):
current_state = open_list.pop(0)
closed_list.append(current_state)
if state.isGoal(current_state):
result = True
break
children = []
addChild(children, current_state)
for child in children:
if state.inOpen(child, open_list):
for e in open_list:
if e.m == child.m and e.c == child.c and e.a == child.a and e.b == child.b:
if child.g < e.g:
e = child
break
else:
open_list.append(child)
# order open_list with the key: f(x) and cost(h(x) small and cost small -> forward)
open_list = sorted(open_list, key = lambda x: x.h)
open_list = sorted(open_list, key = lambda x: x.f)
timeEnd = time.time()
最後就是結果呈現的部分了,如果我們最後open list內所有結點都已經展開了卻還是沒有獲得終點的話,那麼便告訴使用者這樣的組合沒有結果。反之,將結果路徑以及用時給展示出來。
另外在展示結果時記得先將list給反轉,因為我們從closed list中獲得最短路徑時,是從終點到回去起點的,因此必須將結果給反轉,呈現出來的才會是起點至終點的路徑。
設計如下:
if result == True:
print("-" * 50)
print("Missionary Cannibal Boat_A Boat_B state")
answer = state.showResult(closed_list)
answer = reversed(answer)
for e in answer:
e.display()
print("-" * 50)
print("Total cost = ", closed_list[-1].g, ", total nodes = ", len(open_list) + len(closed_list))
print("Time: ", str(round(timeEnd - timeStart, 2)), "sec")
else:
print("The condition doesn't have a solution.")
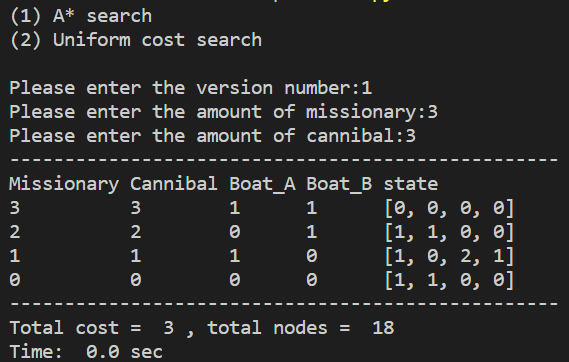
效果如下: